free surgery closed humerus fracture hyderabad private hospitals information.
మన తెలంగాణ/ఆంద్ర్హప్రదేశ్ రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వాలు బి.పి.యల్. కుటుంబాలకు మాత్రమే కాకుండా పింక్ కార్డు దారులు కూడా ఆరోగ్యశ్రీ ఉచిత ఆరోగ్యసేవలను అందించడంకోసం ఏర్పాటు చేసిందే తెలంగాణ ఆరోగ్యశ్రీ...... ఇప్పటికే ఈ పధకం ద్వార అత్యవసర సమయంలో కొన్ని కోట్ల కుటుంబాలను రోడ్డున పడకుంట ఆదుకుంటున్న ఏకైక గొప్ప ప్రభుత్వ పథకం ఆరోగ్యశ్రీ ...
తెలంగాణ/ ఆంద్ర్హప్రదేశ్ రాష్ట్రంలోని ఏ ఓక్క కుటుంబం కూడా ఆపద సమయంలో ఆర్దికంగా నష్టపోకుండా ఉండాలనే దృడసంకల్పంతో ఈ ఆరోగ్యశ్రీ పధకంను రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వం అమలు చేస్తుంది
ఒక్క మాటలో చెప్పాలంటే పేదోడికి ప్రవేట్ వైద్యశాలలు
రెడ్ కార్పెట్ వేసి మరి ఆరోగ్య సేవలను అందిస్తున్నారు అంటే అది కేవలం ఆరోగ్యశ్రీ పధకం ద్వారానే
.
దురదృష్టకరమైన విషయం ఏమిటంటే ఇప్పటికి ఆరోగ్యశ్రీ సేవలను ఎలాపొందాలో తెలియక పోవడం.
ప్రవేట్ హాస్పిటల్లలో ఆరోగ్యశ్రీ కార్డు, వైట్ రేషను కార్డు లేకపోయీనా ఆరోగ్యశ్రీ సేవలను పొందవచ్చు..
THIS SURGERY FREE FOR ALL TELANGANA AND ANDRHAPRADHESH RESIDENCE.....ONLY... UNDER AAROGYASRI
REQUIRED DOCUMENTS;
RATION CARD / VOTER CARD / AADAR CARD / DRIVING LICENSE / SCHOOL ID CARD / AAROGYASREE CARD / CAST CERTIFICATE .
RATION CARD / VOTER CARD / AADAR CARD / DRIVING LICENSE / SCHOOL ID CARD / AAROGYASREE CARD / CAST CERTIFICATE .
.ANY ONE DOCUMENT REQUIRED.
IN HYDERABAD PRIVATE HOSPITALS FREE SURGERY CALL..
.ARCHAEA HEALTH ADVISERS... MALLESH marketing ..9505566617..
Distal Humerus Fractures of the Elbow
The three bones that come together to form the elbow can break (fracture) in different ways. A distal humerus fracture is one type of elbow fracture. The distal humerus is the end of the upper arm bone (the humerus) that forms the upper part of the elbow.
These types of elbow fractures are fairly uncommon. They account for about 2% of fractures in adults.
The elbow is a complicated joint and elbow fractures can involve both of the forearm bones, as well as the humerus.

A distal humerus fracture is one type of elbow fracture.
The elbow is a joint made up of three bones — the humerus, radius, and ulna. It bends and straightens like a hinge. It is also important for rotating the forearm: the ability to turn our hands up (like accepting change from a cashier) or down (like typing or playing the piano).
- The humerus is the upper arm bone between the shoulder and the elbow.
- The radius is one of the forearm bones between the elbow and wrist. When standing with your palm facing up, the radius is on the "thumb side" of the forearm (the lateral side or outside).
- The ulna is the other forearm bone between the elbow and the wrist, running alongside the radius. When standing with your palm facing up, the ulna is on the "pinky side" of the forearm (the medial side or inside).
Bones of the Elbow

The elbow is made up of parts of all three bones in the arm.
The actual elbow consists of portions of all three bones of the arm:
- The distal humerus is the center of the elbow "hinge".
- The radial head moves around the distal humerus and also rotates when the wrist is turned up and down.
- The olecranon is the part of the ulna that "cups" the end of the humerus and rotates around the end of the humerus like a hinge.
Soft Tissues

The elbow is held together by ligaments, muscles, tendons, and the shape of the bones themselves.
The elbow is held together by three main things
- Ligaments connect one bone to another.
- Muscles and tendons work as "leaders" to move the bones around each other.
- The actual shape of the bones themselves hold the elbow together in a stable manner.
Distal Humerus
- The distal humerus is the part of the humerus that "sits" within the "cup" of the ulna, allowing the ulna to move around it. This is elbow motion.
- The distal humerus is able to be felt beneath the skin as a prominent bone, both on the inside of the elbow above the "funny bone" (the ulnar nerve), and on the outside of the elbow.
- The distal humerus makes up the upper part of the actual elbow joint. When it is broken, it can make elbow motion difficult or impossible.

It is common for the distal humerus to break into several pieces. This type of fracture is called comminuted.
A fracture of the distal humerus occurs when there is a break anywhere within the distal region (lower end) of the humerus
Distal humerus fractures are fairly uncommon. They may occur in an isolated manner (that is, there are no other injuries), but can also be a part of a more complex elbow injury.
Distal humerus fractures may occur in a number of ways:
- A direct blow. This can happen during a fall (landing directly on the elbow) or by being struck by a hard object (baseball bat, car dashboard or door during a crash).
- An indirect fracture. This can happen during a fall if a person lands on his or her outstretched arm with the elbow locked straight. The ulna (one of the forearm bones) is driven into the distal humerus, causing it to break.
Distal humerus fractures can be very painful and may prevent the patient from moving his or her elbow. Additional symptoms include:
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Pain or tenderness to the touch
- Stiffness
- Feeling of instability ("my elbow feels like it wants to pop out")
- Pieces of bone may stick out of the skin (rare)
Examination
Doctor exmination
Someone with a distal humerus fracture will most likely go to the emergency room. These types of injuries are very painful and the patient will not be able to move the elbow.
During the examination, the doctor will:
- Examine the skin to see if there are any lacerations (cuts). Bone fragments can break through the skin and create lacerations. This leads to an increased risk of infection.
- Palpate (feel) all around the elbow to determine if there are any other areas of tenderness. This can indicate other broken bones or injuries, such as a dislocated elbow.
- Check the pulse at the wrist to be sure that good blood flow is getting past the elbow to the hand.
- Check to see if the patient can move his or her fingers and wrist, and can feel things with his or her fingers. Sometimes, the "funny bone" (ulnar nerve) may be injured at the same time that the bone is broken, which can result in hand and wrist weakness and numbness.
- The doctor may ask the patient to straighten the elbow. In most cases, the patient will not be able to do this.
- The doctor may examine the patient's shoulder, upper arm, forearm, wrist, and hand, even if the patient only complains of pain at the elbow.
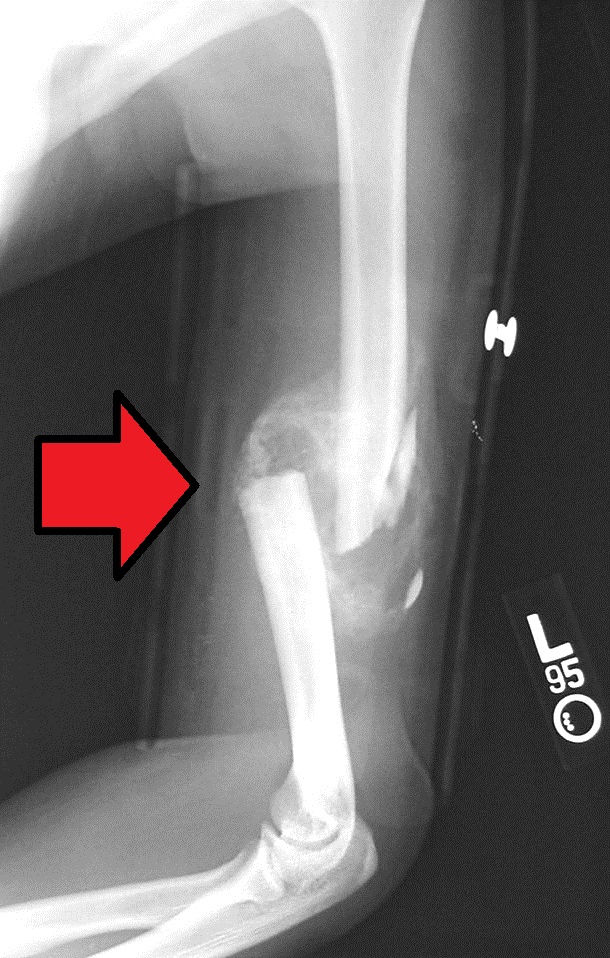
X-rays are the most common and widely available diagnostic imaging technique. X-rays create images of dense structures, like bone. They can show whether a bone is intact or broken. An x-ray of the elbow will be taken to determine if a fracture has occurred.

(Left) An x-ray of a healthy elbow. (Right) In this x-ray, the distal humerus fracture is severely displaced (out of place).
Depending on the patient's symptoms, the doctor may also order x-rays of the upper arm, forearm, shoulder, wrist, and/or hand, These x-rays may reveal more injuries, such as other fractures or dislocations.
While in the emergency room, the doctor will apply a splint (like a cast) to the elbow and provide a sling to keep the elbow in position. Additional immediate treatment will include applying ice to the elbow and giving the patient pain medicine.
Many distal humerus fractures require surgery, but some stable fractures can be treated without an operation. reatment
If the fracture is not displaced, it may require just a splint or sling to hold the elbow in place during the healing process. The doctor will closely monitor the healing of the fracture, and have the patient return to the clinic for x-rays fairly frequently.
If none of the bone fragments are out of place after a few weeks, the doctor will allow the patient to begin gently moving the elbow. This may require visits with a physical therapist.The patient will not be allowed to lift anything with the injured arm for a few weeks.
A nonsurgical approach to a distal humerus fracture may require long periods of splinting or casting. The elbow may become very stiff and require a longer period of therapy to regain motion after the cast is removed.
If the fracture shifts in position, the patient may require surgery to put the bones back together.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery for a distal humerus fracture typically involves putting the pieces of the fractured bone back where they belong. Metal implants — such as plates and screws — are used to hold things in place until the bone is fully healed.
Surgical indications. Surgery is usually necessary when:- The fracture is out of place (displaced)
- The fracture is open (pieces of bone have cut the skin). Because the risk of infection is higher in an open fracture, the patient will receive antibiotics by vein (intravenous) in the emergency room, and may require a tetanus shot. The patient will promptly be taken to surgery so that the cuts can be thoroughly cleaned out. The bone will typically be fixed or replaced during the same surgery. In some cases of severe, open fractures, the doctor may choose to apply an external fixator (bars and pins in the bone outside the surface of the skin) to temporarily hold the bones in place. This gives the skin time to improve before surgery to fix the fracture, and may reduce the risk of infection.
During surgery, the patient may lie on his or her back, side, or stomach. If the patient lies on his or her belly, the face (lips, eyelids) may be swollen for a few hours after the operation is over. This is normal and temporary.

The broken bones have been put back together and are held in place with a combination of plates and screws.
The surgeon will typically make an incision over the back of the elbow to reach the fractured bone. There are several ways to hold the pieces of bone in place. The surgeon may choose to use:
- Pins/wires
- Screws only
- Plates and screws
- Sutures ("stitches") in the bone or tendons
- A combination of the above methods
The incision is typically closed with sutures or staples. Sometimes, the surgeon will place a splint on the arm to help take stress off the incision.
Surgical considerations. Different fractures may require specific considerations during the procedure.- Ulnar nerve placement. In most cases, the surgeon will need to gently move the ulnar nerve ("funny bone") to prevent it from being injured during surgery. At the end of the procedure, the ulnar nerve will be put back in place or moved to a slightly different position. This is decided by the surgeon during the procedure, and is usually done to prevent nerve symptoms from occuring in the future.
- Bone loss. If some of the bone is missing or crushed beyond repair (pieces of bone lost through a wound during an accident), the fracture may require bone filler. Bone filler can be bone supplied by the patient (typically taken from the pelvis) or bone from a bone bank (from a donor), or an artificial calcium-containing material.
- Osteotomy. Sometimes, the tip of the elbow (olecranon) will be cut so that the surgeon can see the bone fragments. The cut bone is moved out of the way during fracture repair. After the fracture is repaired, the cut olecranon is returned to its original location and repaired.
- Elbow replacement. If the distal humerus fracture is too severe to fix properly (as often occurs in elderly patients), the elbow may need to be replaced. This procedure is similar to a hip or knee replacement. A metal and plastic implant is attached to the humerus after the broken bits of bone are removed. Another metal and plastic implant is attached to the ulna (forearm bone), and the two implants are connected to form a hinge. These implants may be held in place with bone cement.
- Infection. There is a risk of infection with any surgery, whether it is for a distal humerus fracture or another purpose.
- Pain associated with surgery. Pain is controlled in the operating room by an anesthesia team, who can either put the patient to sleep or numb the arm, or both. The doctor will discuss the method of anesthesia with the patient prior to surgery. After surgery, pain is controlled with a combination of pain medications, such as morphine and codeine, and acetaminophen.
- Damage to nerves and blood vessels. There is a minor risk of damage to nerves and blood vessels around the elbow. This is an unusual side effect. Although the ulnar nerve is moved during surgery, it typically recovers. Temporary numbness or weakness in the area may occur. This may take weeks or months to disappear. In rare cases, the nerve may be injured during surgery, and further surgery may be required to help the nerve recover.
- Nonunion. Surgery does not guarantee healing of the fracture. A fracture may pull apart, or the screws, plates, or wires may shift or break. This can occur for a variety of reasons, including:
- The patient does not follow directions after surgery.
- The patient has other health issues that slow healing. Some diseases, like diabetes, slow healing. Smoking or using other tobacco products also slow healing.
- If the fracture was associated with a cut in the skin (an open fracture), healing is often slower.
- Infections can also slow or prevent healing. If the fracture fails to heal, further surgery may be needed.
Where is office located.A person can't have enough capital for his child.can you suggest free service for bone fracture through aadhar card. Let know details
ReplyDeleteThank you so much for the information. This article describes the problems of shoulder pains. For more related information you can visit here frozen shoulder treatment in hyderabad
ReplyDelete